Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
- Chlamydia trachomatis is the main bacterial agent responsible for urogenital chlamydia. This STI can cause various genital symptoms, especially in women, although many patients are asymptomatic carriers without knowing it. However, early detection allows effective treatment with antibiotics.
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococcus) is a highly transmissible bacterium responsible for gonorrhea. In women, these gonococcal infections are often silent or do not produce recognizable clinical signs until complications develop.
- Genital mycoplasmas are tiny bacteria that are widespread in the environment. For Mycoplasma genitalium, its detection is considered clinically significant. In women, Mycoplasma genitalium is involved in various conditions of the female genital tract, including cervicitis, urethritis, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Trichomonas vaginalis is a human protozoan parasite responsible for a generally mild sexually transmitted infection. Trichomoniasis typically causes vulvovaginitis with often heavy vaginal discharge, variable in odor, with a foamy appearance and a greenish, sometimes whitish, color.

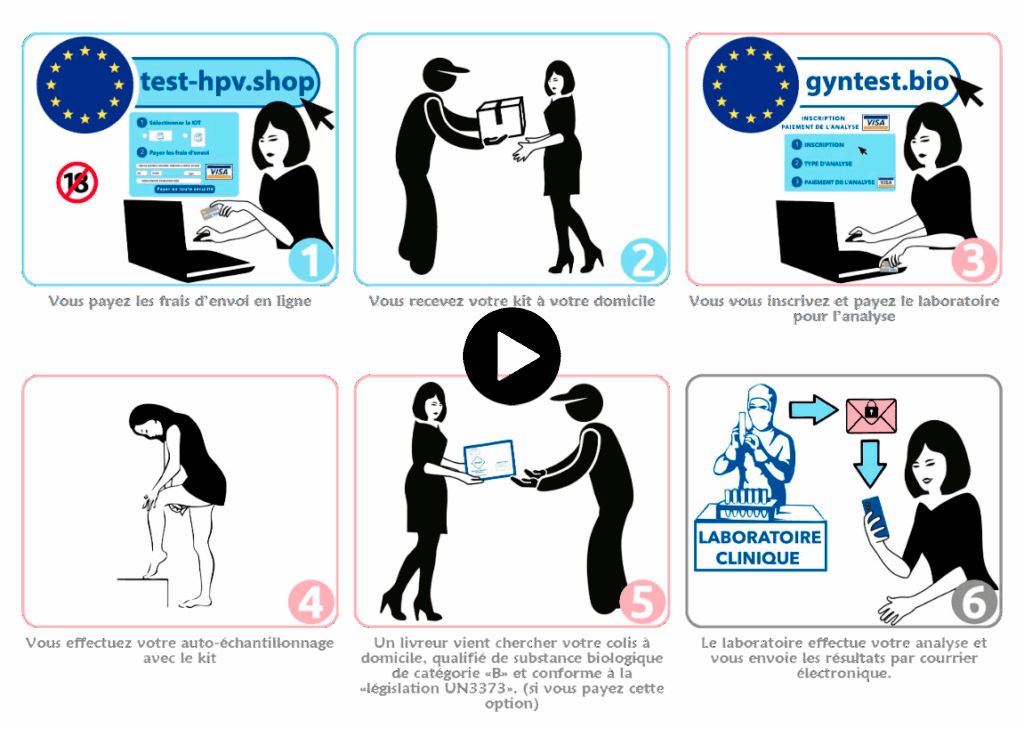
Your sample is analyzed by a French medical laboratory accredited by COFRAC, with results certified by a medical biologist.